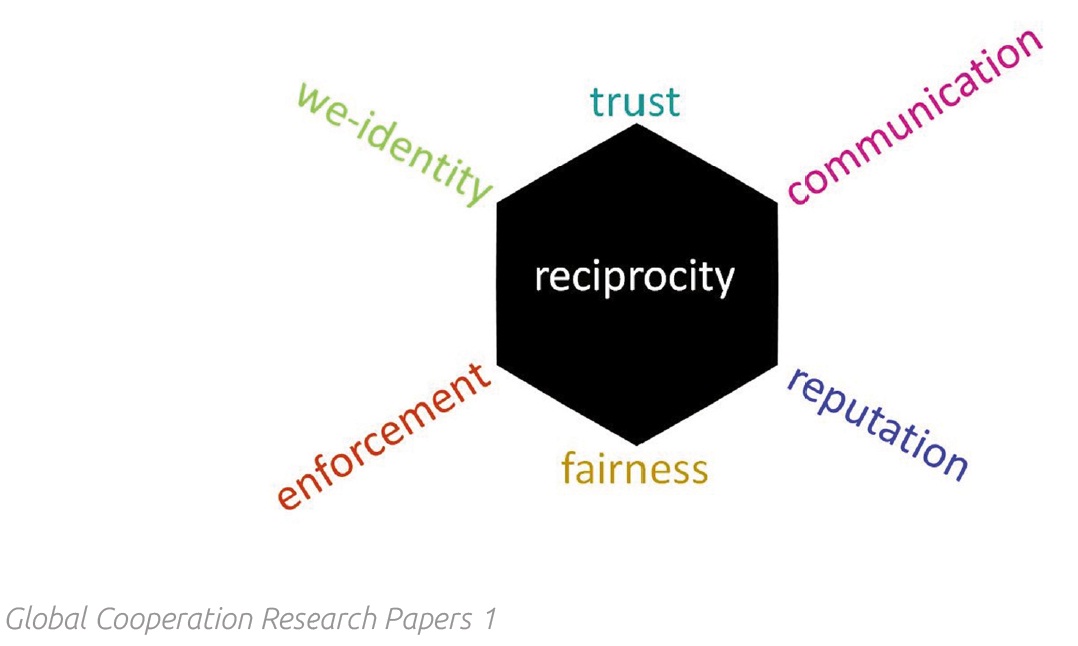
I am super-happy, that the Agence Française de Développement (AFD) through Jan Krewer has managed to shed some light on a crucially under-researched topic: How are digital commons in Sub- Saharan Africa doing? Which resources are governed through a commons-approach on the continent? How important are they and how are their communities functioning? Although the study makes it clear that it did not intend to map all existing digital commons in Sub-Saharan Africa, I find it the most extensive listing that has ever been done listing a total of 89 examples. And I have tried to find such listings or mappings or compendiums or directories for a while, see for instance this article. So KUDOs to Jan and AFD.
On top of mapping the digital commons the study contains 10 short case studies based on interviews, namely African Storybook (Open Educational Resources), AfricArXiv (Content and data), AFRINIC (Norms and standards), Energypedia (Content), Grassroots Economics (Digital financial assets), Open MRS (Free software for health information management), Pamoja-Net (Digital equipment), Ushahidi (Open source
software and data), WaziHub (Free software, open plans and designs), Wikimedia Ivory Coast (Content).




































 Some critics argue that
Some critics argue that